Research and development for drug discovery underlining the need for supercomputers in pharmaceuticals
Drug discoveries usually stretch up to years and decades without an assurance of emerging victorious. Subsequently, only a small proportion of the research and development succeed in transporting the drugs from the laboratories to the medicine shops. Healthtech innovations necessitate the employment of advanced technology as they tend to assist the process accurately. Similarly, supercomputers in pharmaceuticals have immense potential to aid research and development intended for drug discovery. To enable the researchers and medical professionals engaged in pharmaceuticals to produce optimum solutions without enduring maximized failures, supercomputers in pharmaceuticals are introduced. This would save money and time causing the pharmaceuticals to invest in supply-chain management and availability.
Why Supercomputers?
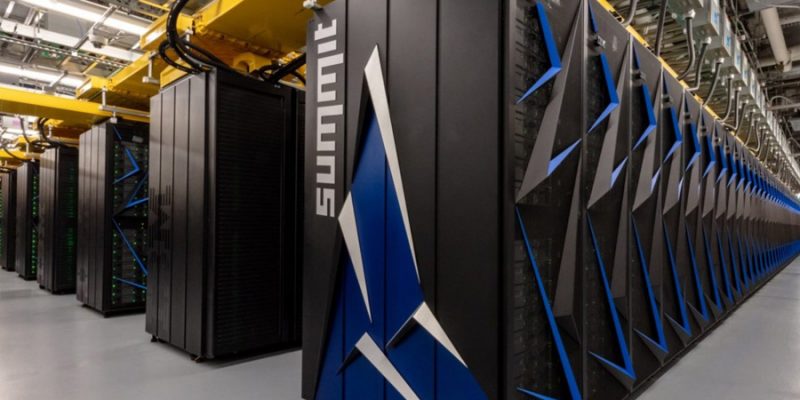
The supercomputers do not function anywhere near to the general-purpose computer owing to its supremacy imbibed. Supercomputers in pharmaceuticals are increasingly appreciated for supporting massive and endless sets of data intensively. Furthermore, accelerating the process of analysing and interpreting data to move forward with the research and development of pharmaceutical products. The creation of new drugs and therapies involving artificial intelligence and machine learning has resulted in greater efficiency and accomplishment than before. Simplifying and arranging complex systems and big data respectively makes supercomputers in pharmaceuticals a boon.
Assisting the Data-Driven Methods
The practice of implementing research into reality includes various forms of data-driven methods that examine molecules, dynamic modelling of the conclusion, analysing, and performing virtual trials. Supercomputers in pharmaceuticals efficiently prove their competency constantly by informing the researchers about any errors and changes in the work instantly. The data is thoroughly assessed to yield the best results and extract the prime essence as fast as possible.
Determining The Unknown
Advanced technology like supercomputers in pharmaceuticals can essentially identify dormant cases of critical causes of death. Often an underlying brain disease or cancer goes unidentified by doctors. The stealth traits of DNA residing in numerous human bodies do not turn up in various diagnostic tests. Therefore, researchers are stressing about finding out the theory that goes behind such an instance. In this process, supercomputers can contribute to reading millions of pathological images and interpreting them for the researchers, further, aiding them in effectively recognizing the in-detailed variations. Allocating a single drug against these variations is a necessity which again becomes tedious as placing and assessing the same drug against thousands of variations is time-consuming. To save time and avert these supercomputers can perform that for them manifesting the side effects and need for altering the elements of the drugs.
Computerized Drug Discovery
Computer-Aided Drug Discovery and Design (CDDD) is a popular phenomenon that employs the existing drugs to construct new drugs in times of crisis and immediate requirement. A faster way of drug discovery empowered by the healthtech innovation of supercomputers in pharmaceuticals has now evolved into assisting in almost every phase of developing a prescription. Research and development of pharmaceuticals now witness potential progress in various fields such as management, analysis, examining, and validating the developing solution. Therefore, this emergency model combined with supercomputers can yield cumulative results in drug discovery.
Some Supercomputers in Pharmaceuticals
- MDGRAPE-4A was developed by RIKEN Centre to perform molecular dynamics and conduct trials of crucial drugs through modelling.
- Cambridge-1 by NVIDIA, which is optimized to use AI and simulation to ease out the medical challenges for research and development teams.
- Besides, EuroHPC and ExCAPE are also amidst an ongoing process to create supercomputers in pharmaceuticals that can ramp up the process of precision medicines.